Resin based restoration two surfaces posterior – Resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior marks a significant advancement in the field of dentistry, providing a comprehensive solution for restoring damaged teeth. This technique, meticulously detailed in this article, empowers dental practitioners with the knowledge and skills to achieve optimal oral health outcomes for their patients.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Resin-Based Restoration for Two Surfaces Posterior: Resin Based Restoration Two Surfaces Posterior
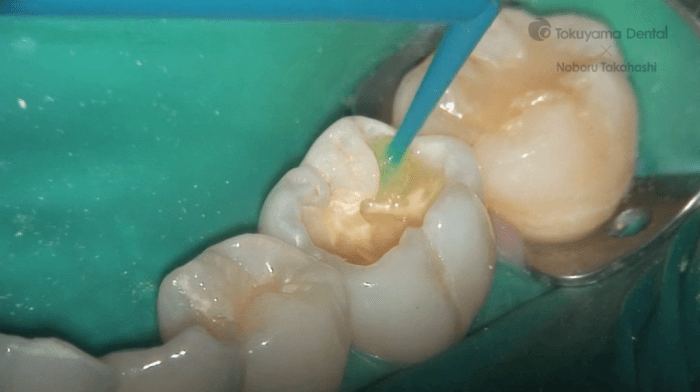
Resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior is a technique used to repair damaged or decayed teeth that involve two surfaces of the posterior teeth, which are the molars and premolars. This type of restoration utilizes resin-based materials, such as composite resins or compomers, to restore the tooth’s structure and function.
Understanding the properties and techniques associated with resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior is essential for achieving successful and long-lasting results. This article will provide an overview of the materials, equipment, clinical procedures, advantages, disadvantages, and clinical considerations involved in this restoration method.
Materials and Equipment
The materials used in resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior include:
- Composite resins:These are tooth-colored materials that are composed of a resin matrix and filler particles. They are used to restore the shape and color of the tooth.
- Compomers:These are a hybrid material that combines the properties of composite resins and glass ionomer cements. They release fluoride and have good bonding strength to dentin.
The equipment used in resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior includes:
- Dental handpiece:This is used to prepare the tooth and remove any decay.
- Dental burrs:These are used to shape the tooth and create a space for the restoration.
- Etching gel:This is used to etch the tooth surface to create a stronger bond between the restoration and the tooth.
- Bonding agent:This is used to create a chemical bond between the restoration and the tooth.
- Light-curing unit:This is used to cure the resin-based material.
Clinical Procedures
The clinical procedures for resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior involve the following steps:
- Tooth preparation:The tooth is prepared by removing any decay and shaping the tooth to create a space for the restoration.
- Etching:The tooth surface is etched with an etching gel to create a stronger bond between the restoration and the tooth.
- Bonding:A bonding agent is applied to the tooth surface to create a chemical bond between the restoration and the tooth.
- Placement of the restoration:The resin-based material is placed into the prepared tooth and shaped to restore the tooth’s anatomy.
- Light-curing:The resin-based material is cured with a light-curing unit to harden the material.
- Finishing:The restoration is finished by removing any excess material and polishing the surface.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior offers several advantages, including:
- Esthetics:Resin-based materials are tooth-colored, which makes them a good choice for restoring teeth that are visible when smiling or speaking.
- Strength:Resin-based materials are strong and durable, which makes them a good choice for restoring teeth that are subject to heavy wear and tear.
- Versatility:Resin-based materials can be used to restore a variety of tooth defects, including cavities, fractures, and chips.
However, resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior also has some disadvantages, including:
- Polymerization shrinkage:Resin-based materials shrink slightly when they are cured, which can lead to gaps between the restoration and the tooth.
- Wear:Resin-based materials can wear over time, especially if they are not properly maintained.
- Cost:Resin-based restorations are more expensive than some other types of restorations, such as amalgam fillings.
Clinical Considerations
When considering resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Patient selection:Resin-based restorations are not suitable for all patients. Patients who are at high risk for developing recurrent decay or who have poor oral hygiene may not be good candidates for this type of restoration.
- Tooth condition:The condition of the tooth will also affect the success of a resin-based restoration. Teeth that are severely decayed or weakened may not be able to support a resin-based restoration.
- Long-term prognosis:The long-term prognosis of a resin-based restoration will depend on a number of factors, including the patient’s oral hygiene, the condition of the tooth, and the skill of the dentist.
Case Studies
Several case studies have demonstrated the successful use of resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior. One study found that resin-based restorations had a success rate of over 90% after five years.
Another study found that resin-based restorations were more effective than amalgam fillings in preventing recurrent decay.
Conclusion, Resin based restoration two surfaces posterior
Resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior is a versatile and effective technique for restoring damaged or decayed teeth. However, it is important to understand the properties and techniques associated with this type of restoration in order to achieve successful and long-lasting results.
Query Resolution
What are the key advantages of resin-based restoration for two surfaces posterior?
Resin-based restorations offer superior aesthetics, durability, and versatility, allowing for precise restoration of damaged teeth.
How does resin-based restoration compare to other restorative techniques?
Resin-based restoration provides comparable or superior outcomes to traditional amalgam fillings, offering better aesthetics and bonding strength.